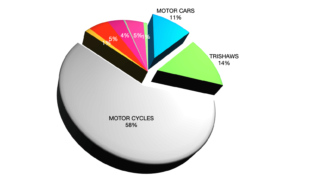
| Private enterprise as an environmental villain Private enterprise, and industry in particular, has long been criticised for sacrificing the environment to the pursuit of profits. For many critics, the polluted industrial city symbolises this environmental disregard, with its factories consuming scarce natural resources, and then belching out smoke, pouring out liquid effluents, and dumping hazardous solid wastes. De-industrialisation and tighter environmental regulation in the North have greatly reduced these very visible symptoms of urban environmental degradation. In the South, however, there are many cities where uncontrolled industrialisation still causes severe air, water and land degradation. The resulting environmental damage is often blamed on the inherent greed of private enterprise. Private enterprise as an environmental saviour Defenders of private enterprise point out that the bulk of this industrial pollution comes from a comparatively small set of industries, and there is no evidence that these industries are less polluting when they are publicly owned. Moreover, given the right economic signals, the pursuit of profits can stimulate the search for cleaner technologies and production processes. A small but increasing number of private enterprises actually make their profits by helping others to improve their environmental performance. Even companies in polluting industries are beginning to try to change their image from environmental villains to partners in the search for environmental improvement. And there are business leaders who argue that well designed environmental standards can stimulate efficiency improvements and make firms more competitive. Indeed, pro-business publications often present the entrepreneurial drive of private enterprise as the key to environmental improvement. Getting the best from the private sector Both of the perspectives noted above have some truth. Ultimately, however, the private sector is neither the underlying reason for urban environmental burdens nor the solution. The key question is not whether but how the private sector can be made to contribute more to urban environmental improvement. Moving towards sustainable industrial production Environmentalists often advocate a holistic approach to environmental risk management that takes into account all of the environmental burdens associated with every phase in a product’s lifecycle, and generally favors changes in the production process over end-of-pipe measures, containment, dispersal or remediation. In the affluent North, cleaner production is often promoted as a means of achieving environmental sustainability without undue sacrifices in consumption. In the South, where much of the population needs more rather than less consumption, cleaner production holds out the hope of achieving a shift towards greater economic efficiency and higher production levels, while also keeping down environmental burdens. As with pro-poor public-private partnerships, however, this hope will not be easy to realize. As indicated in the table pollution control and increased efficiency are themselves only two steps on the way to what many environmentalists would be willing to call sustainable industrial production. More radical visions foresee a time when firms will be engaged in lifecycle management, cities will promote eco-industrial estates, and nations will take an integrated approach to pollution control. Some even look forward to a time when emissions will be negligible and producers will be responsible for all of the environmental consequences of their actions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In many cities, one of the first steps towards improving urban ambient environments is to target the major polluters and their most harmful pollutants. Improvements can generally be verified with relatively inexpensive ‘end-of-pipe’ monitoring and on-site inspections. A common second step is to require environmental impact assessments for potentially polluting industries. Both of these steps are more likely to be effective when accompanied by a more systematic monitoring of the urban environment, including concentrations of selected air and water pollutants at selected sites within the city. This can serve not only to inform government and industry but can help to engage a wider public in discussions of pollution problems. The table following summarizes the environmental impacts of several of the worst offenders. Many of these industries tend to be concentrated in urban areas, and often they account for a large share of industrial pollution. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| There are known technologies that can at least eliminate the worst excesses. A number of factors can complicate industrial pollution control in Southern cities:
Nevertheless, once the need to protect local residents from hazardous pollution is recognized, a great deal can usually be done at relatively low cost, provided the interests of all major stakeholders are taken into account. Addressing highly dispersed pollution, and especially those from non-point sources, is generally more difficult. Moreover, the so-called end-of-pipe technologies favored in the early stages of pollution control often change the form of the pollution rather than eliminate it. Thus, for example, tall stacks merely displace air pollution over greater areas, while scrubbers remove pollutants from the air, often leaving a highly toxic sludge. Both technologies may reduce the exposure levels for local residents but neither provides a long-term solution. From a clean technology perspective, once the simple measures to reduce the most hazardous pollutants have been taken, the next operational pathway to environmental improvement is efficiency improvement. Material and energy efficiency is generally associated with lower environmental impacts and can often yield cost savings. Often, higher efficiency brings greater productivity along with waste reduction. At least superficially, cleaner production would seem to hold out the hope of increasing the production of marketable goods, while reducing the creation of environmental ‘bads’. In practice, ecological efficiency and economic efficiency are not identical goals. In most cases, some groups will lose out when more ecologically efficient production processes are introduced. In many cases ecological efficiency (or, for that matter, economic efficiency correctly defined) is not economically competitive in existing markets, and requires tighter regulation and stronger economic incentives, as well as a willingness on the part of both private enterprises and the government to take environmental costs seriously. In some cases, forcing industries to adopt ecologically efficient technologies can cause severe economic disruptions. Good government regulation (both national and local), public-private partnerships and selective pressure from civil society are all needed to help ensure that the choices made reflect the public interest, and not merely those of the most vocal or powerful stakeholders. They are particularly important in poor cities, where the vulnerability to environmental hazards is high, but economic disruptions from heavy-handed regulation can also cause severe hardship. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Registration with the Sri Lanka FINANCIAL CHRONICLE
 would enable you to enjoy an array of other services such as Member Rankings, User Groups, Own Posts & Profile, Exclusive Research, Live Chat Box etc..
would enable you to enjoy an array of other services such as Member Rankings, User Groups, Own Posts & Profile, Exclusive Research, Live Chat Box etc.. All information contained in this forum is subject to Disclaimer Notice published.
Thank You
FINANCIAL CHRONICLE

www.srilankachronicle.com

 Home
Home