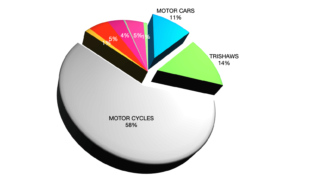
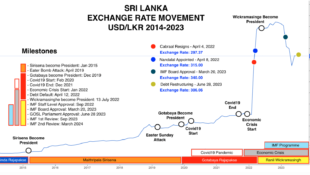
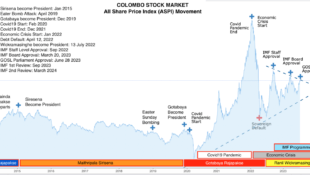
Legal framework for Related party transactions in Banks in Sri Lanka are as follows.
Transactions between affiliates
Which legal and regulatory limitations apply to transactions between a bank and its affiliates? What constitutes an ‘affiliate’ for this purpose? Briefly describe the range of permissible and prohibited activities for financial institutions and whether there have been any changes to how those activities are classified.
Affiliate is referred to as ‘related party’ under Sri Lankan law.
Section 3(7) of the Banking Act Direction No.11 of 2007 (for LCB) and Banking Act Direction No.12 of 2007 (for LSB) requires the bank’s board to avoid any conflicts of interest that may arise from any transaction of the bank with ‘related parties’ and to ensure that ‘more favourable treatment’ is not given to them.
Related parties are:
- any of the bank’s subsidiary companies;
- any of the bank’s associate companies;
- any of the directors of the bank;
- any of the bank’s key management personnel;
- a close relation of any of the bank’s directors or key management personnel;
- a shareholder owning a material interest in the bank; and
- a concern in which any of the bank’s directors or a close relation of any of the bank’s directors or any of its material shareholders has a substantial interest.
Types of transactions covered include:
the grant of any type of accommodation, as defined in the Directions on maximum amount of accommodation;
the creation of any liabilities of the bank in the form of deposits, borrowings and investments,
the provision of any services of a financial or non-financial nature provided to the bank or received from the bank; and
the creation or maintenance of reporting lines and information flows between the bank and any related parties which may lead to the sharing of potentially proprietary, confidential or otherwise sensitive information that may give benefits to such related parties.
‘More favourable treatment’ includes granting of ‘total net accommodation’, exceeding a prudent percentage of the bank’s regulatory capital, as determined by the board, charging lower interest or paying more than the bank’s deposit rate for a comparable transaction with an unrelated comparable counterparty; providing preferential treatment or providing or receiving services without an evaluation procedure.
Most banks are listed with CSE and are also expected to comply with the CSE’s related-party transaction regulations.
 would enable you to enjoy an array of other services such as Member Rankings, User Groups, Own Posts & Profile, Exclusive Research, Live Chat Box etc..
would enable you to enjoy an array of other services such as Member Rankings, User Groups, Own Posts & Profile, Exclusive Research, Live Chat Box etc.. 
 Home
Home